Why Store Layout Matters in Retail
The layout of a retail store carries several internal and external business implications.
Layout is an important physical aspect of branding efforts. It creates an opportunity to create the desired atmosphere in stores thereby helping to create brand perception and establish an emotional connection with customers. These two go a long way in customer attraction and retention. Retailers for whom branding is an important component of their business vision take layout planning seriously. If the expertise is not available internally, the option of availing layout planning services from the outside is always there.
The store layout defines a large chunk of what customers experience when they are physically present in a store. It affects the flow and navigation of customers within a store. A good layout plan allows smooth movement and makes it easier for customers to locate products. This movement factor also has operational implications. It affects the movement of employees when they are executing their back-end or front-end operations.
By focusing on product placement and visibility, retailers can encourage customers to explore more products and enhance opportunities for sales. The placement of complementary products in close proximity serves as an example here. For instance, breakfast products like cornflakes, oats, and milk could be neighbours in a departmental store. This principle applies to retail stores with extensive merchandise like grocery or departmental stores.
Layout also plays a vital role in inventory management. A good layout plan allows for proper and convenient classification of zones and shelves and easy access for stacking the shelves. The chances of misplacement or any other reason for shrinkage are also reduced when the layout is well-organised. For example, there should be sufficient space between aisles to safely stack products on the top shelves.
Store layout is something that cannot be changed too often. Without vision and planning, things can go wrong. By having a plan, room for accommodating temporary changes in merchandising can be made. This may not apply to the entirety of a store but there are circumstances when retailers have to make improvisations in their merchandising strategies. For example, in festive seasons, room to accommodate certain new product categories may have to be made by shelf-shifting of inventory.
Layout planning allows suitable incorporation of various important accessibility and navigational features. This includes the presence and visibility of signages, sufficient dimensions of the aisles, safe placement of electrical wires and AC vents, door opening/closing space, access to shopping carts, etc.
In starting online sales, brick-and-mortar retail stores also need to make up for the additional space requirements for their online order fulfilment. The processes and systems required for fulfilling online sales are different from the ones involved in traditional store-based retailing. Some of the resource requirements may overlap with the existing capabilities but many new requirements emerge. For example, a designated space is required for packaging orders and placing them for final delivery. These considerations must find a place in layout planning as doing the same can get challenging later on.
In short, a carefully planned retail store layout contributes to/helps in
- Better branding
- Improved customer experience, in-store shopping experience
- Opportunity to drive more sales
- Smooth operations, smooth movement of people and inventory
- Organised inventory management
- Adapt to changing merchandising requirements (demand, trend)
- Deployment of safety and security measures
- Establishing online sales channels
Important Considerations in Retail Store Layout Planning
Customers’ Needs and Expectations
Understanding what customers want is one of the fine-level considerations in layout planning. Sometimes even big retail brands have to localise their layout as per the prevailing demand and expectations. For example, a branded restaurant in a crowded marketplace area is likely to think along the lines of accommodating more customers as a priority. A branch of the same restaurant on a highway may think differently about its layout.
Nature of Products
The nature of the products offered has a direct bearing on layout planning. Factors like product size and weight, storing requirements, etc. affect the specifics of a layout plan. For example, the aisle space needed for moving refrigerators is much higher than the same for microwave ovens. In the same context, it would be much more difficult to move bulky items like refrigerators between floors.
Zone Classification
Creating zones is something fundamental. It keeps things organised. It is easy to operate in an organised space whether it is a store or a warehouse or an office. It is common to see this zone-based segregation of space in every big and small retail store. How zones are created in retail stores varies. For example, zone classification is usually done on the basis of function in small stores. In such stores, there may be one or two display counters manned by sales executives. In bigger stores, zones are classified on the ground of product categories. This is typical in departmental stores.
Product Placement
Product placement facilitates the shopping decisions of customers. There may be additional intentions but the essence is the same which is to make it easy for customers to spot what they need and give them a more fulfilling experience. For example, all products associated with kitchen cleaning can be grouped together on one shelf. Clearly, these considerations affect layout plans.
Entrance and Exit
The entrance and exit points of a store must not be blocked. They can be fancy or more but just not be blocking in any manner. For example, if customers’ entry is slow (say during busy hours), it creates a psychological disruption or barrier. The same holds true while exiting a store. It forms a part of the overall shopping experience for customers. In layout planning, these two important factors should be addressed.
Checkout
In most stores, entry, checkout, and exit are in close proximity. This is okay only as long as the flow of traffic to or from any of these points is not crossing one another. Some customers may not even buy anything but still their movement should also be taken into consideration. There should be room for extended checkout queues in the event of any technical or other operational snag. Incorporation of safety and security measures is also an important factor here.
Motion Analysis
Motion analysis is specifically useful in restructuring store layouts. It is the study and analysis of how customers naturally move within a store. It can shed light on many relevant insights like which aisles are first chosen, which areas of the store remain most busy, the flow of movement from start to end, etc. These and other insights derived from this study help in making the necessary improvisations in the layout for delivering a better in-store shopping experience to customers.
Ratio between Empty and Occupied Space
The more spacious a store looks the better the shopping experience tends to be. Spacious stores are preferred over congested ones. Given the element of space constraint, it is challenging to achieve this objective. The way out is to establish a desired ratio between empty and occupied space in advance and follow the same in planning the rest of the layout elements.
Room for Valued-Added and Essential Facilities
Facilities in a retail store can include restrooms, waiting areas, sitting spaces, lactation rooms, etc. Different stores offer different facilities. Some of these facilities can also be a component of value propositions. The point is to plan for the strategic and spatial requirements of these facilities. Many small businesses ignore this component. They should at least consider providing some of the essential facilities within the same compound with due consideration to hygiene & maintenance and safety & security standards.
Special Attention to the Differently-Abled
Making a store suitable for access to all customers not only presents a brand in a good light but is also a very humane consideration. It should not be a part of any strategy and come naturally. The facilities or provision should also not be incomplete. At least the big and responsible retail brands should not disappoint on this parameter.
Hygiene & Maintenance
Hygiene and maintenance affect customers, employees, and brand impression making these two vital considerations in retail store layout planning. It allows for the proper establishment and better management of systems required to maintain a safe and sparkling store environment. For example, cleaning equipment must easily go through the aisles and other parts of the store. There should be proper shielding of the store from outside dust and wind. Maintaining SOPs for cleaning and maintenance operations is a must.
Safety and Security
Safety and security considerations are important in retail stores for many reasons affecting customers, employees, inventory, and overall business. Addressing the safety and security concerns at the time of layout planning helps incorporate the necessary systems from the onset. Some of the vital safety and security deliberations are listed below:
- Maximising visibility with proper lighting, having long and open spaces, avoiding risky structures, use of mirrors, etc.
- Installation of CCTV camera systems covering the entire store and the store compound and perimeters.
- Development and display of SOPs to be followed in case of emergency situations
- Installation of fire alarms and water sprinkler solutions/systems
- First-aid kit or box, prominent display of list of emergency telephone numbers
Schedule Review
As layout planning experts, we always stress that store layout is not a fit-and-forget event. Review of existing layouts helps retailers make necessary adjustments and optimise the layout to better reflect customer and business prerogatives. It should be also seen if any new business decision or activity has any impact on the store layout.
The considerations taken up in layout planning vary from business to business. However, the objectives are more or less the same for all. Giving a top-notch in-store shopping experience to customers, space optimisation, support to business operations, and adherence to safety are the easy top picks.
Once the store layout requirements are established, the awareness of the different layout options commonly adopted by retail brands and businesses is helpful to quickly move to a suitable layout solution with or without customisations.
Retail Store Layouts (Plans/Options)
Coming to layout options, there are six popular models available. Each of these models has its unique pros and cons. These retail store layout plans are discussed ahead.
Grid Layout
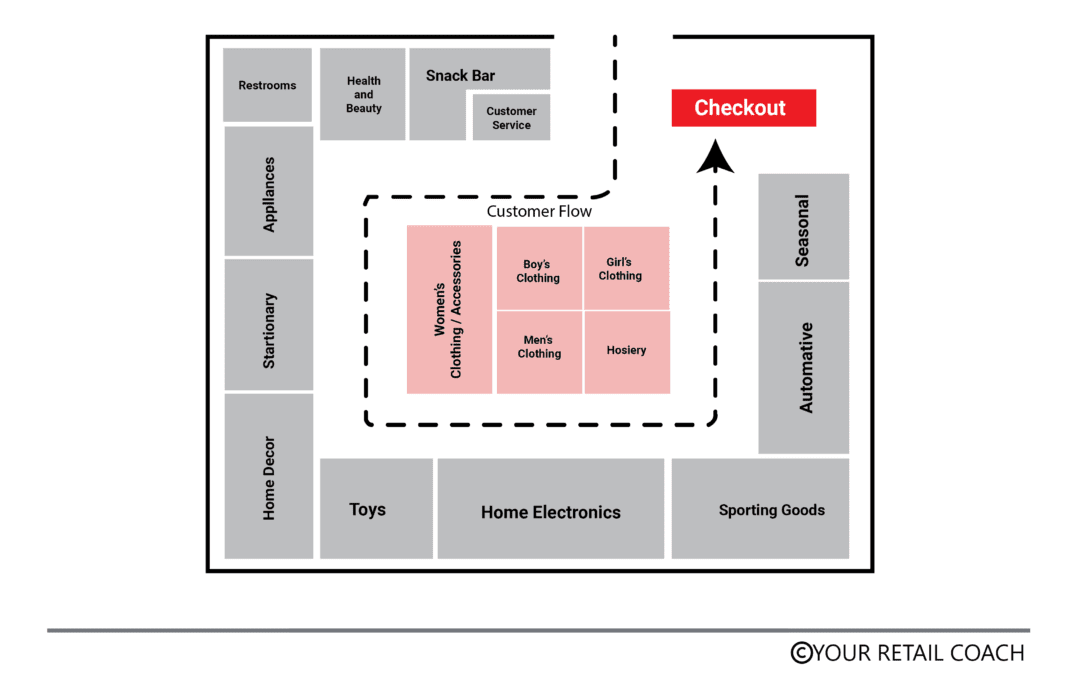
As the name itself suggests, in grid layout, the racks or shelves are placed in straight and/or parallel formations. It is the simplest and most commonly used store layout model. It presents an organised arrangement facilitating easy navigation for customers. Grid layout is common for grocery and departmental stores. It suits stores with an extensive range of products. The underlying emphasis here is on product visibility and the extensiveness of merchandise display. Other features of grid layout are simplicity, order, space optimization, visibility, and uniformity.
A problem that silently surfaces in a grid layout is that it becomes monotonous. Customers’ inclination to visit such stores may lessen with time. They can get attracted to new stores. Another problem is that the scope of showcasing products differently is limited in this layout. These problems can be addressed by making visually attractive alterations (lighting, adding themes) from time to time.
Racetrack or Loop Layout
In a racetrack or loop layout, the arrangement of furniture and fixtures is done in such a way that the navigation through a store forms a circular or oval flow pattern. It lets customers explore the entire store with a sense of flow and direction. Shelves are placed along the in-perimeter as well as in the central areas of a store creating room for space optimization. The scope of innovation with the interiors is high in this layout model.
A racetrack or loop layout is ideal for retail stores with large spaces. Trying to create a loop layout with a small space may end up with poor visual appeal and inefficient utilisation of space. The racetrack layout is not for ordinary shopping. It is ideal for shopping that requires a certain degree of exploration (e.g. fashion, jewellery). An inherent problem with this layout is that it makes turning back difficult for customers and also disrupts the movement of other customers.
Free-Flow Layout
In a free-flow layout, sometimes also called organic layout, no customary pattern is followed. Furniture and fixtures are placed without adhering to any visible pattern. However, it is also not done arbitrarily. The idea in hindsight is to present an open and flexible shopping experience. This layout can be found in trade, auto, and technology fairs. Luxury retail stores often don this layout. The free-flow layout goes beyond the racetrack layout when it comes to the element of exploration.
While a free-flow layout is good for exploration, done wrong and it can be distracting for customers and can eventually result in no purchase. The probability of quickly shifting customers’ attention from one product/shelf to another is always high in free-flow layout patterns.
Diagonal Layout
The diagonal layout is the slash or backslash version of the grid layout. Here, the shelves are parallelly arranged at an imperfect angle. On a lighter vein, the diagonal layout is the vacation sought by the grid layout. The idea is to do something to keep things interesting and visually appealing. However, a diagonal layout is a good solution for floor areas that are not perfectly square or rectangular. This layout works well with reasonable floor sizes.
Surely, diagonal arrangements can spice things up a bit (good for fashion stores, wine shops, and supermarkets) but they can also be distracting and make finding products difficult for customers. It is not suitable for purchases that could be also done in a hurry. The movement is not always smooth in diagonal layouts.
Angular Layout
Angular layout floor plans are marked by curved or angular fixtures and the flow of traffic. Imagine the solar system (not on scale) drawn on a piece of paper. There are shelves or display units of curved or angular shapes of different sizes placed at different parts of a store. This also makes the flow of traffic curved or angular. The emphasis in angular layouts is primarily on branding, delivering a unique display and in-store shopping experience to customers. Luxury fashion (also niche fashion like groom and bridal wear) and concept stores fit well into the angular layout strategy. The features of this layout make it highly specific to only a few retail categories. Unless it is wrongly planned and implemented or mistakenly chosen, pointing out its negatives would be unjust.
Hybrid Layout
The hybrid layout is a combination of two or more of the other layouts. It features flexibility and customization. The layout can be tailor-made to suit the unique requirements and constraints of each business. A hybrid layout suits small businesses that do not have enough space to deploy any one other layout plan in its entirety. The hybrid layout is also suitable for retail startups that have the layout as an integral part of their branding and value proposition. A unique advantage of a hybrid layout in large spaces is that it allows the creation of different layout plans for different sections within a store. An ideal incumbent would be retail sports accessories businesses.
Hybrid layouts call for careful planning – more than in the case with any other retail layout strategy. The coming together of the elements of many different layout models evokes the chances of incoherence in brand comprehension and overall impression and experience delivered to customers.
Recap
The layout of a store has many internal and external business implications. Not planning for it can go the wrong way for a business. By careful planning and implementation, store layout can become an impactful platform to create favourable circumstances for business. Some of the important aspects of business and marketing that can be positively altered in favour via proper layout planning are branding, customer experience, sales, operations, inventory management, response to competitive or market changes, and safety and security.
Some of the critical factors for consideration in layout planning are:
- Customers’ Needs and Expectations
- Nature of Products
- Zone Classification
- Product Placement
- Entrance and Exit
- Checkout
- Motion Analysis
- Ratio between Empty and Occupied Space
- Room for Valued-Added and Essential Facilities
- Special Attention to the Differently-Abled
- Hygiene & Maintenance
- Safety and Security
- Schedule Review
After the store layout prerogatives are established, the awareness of the different layout models commonly used by retail brands and businesses helps to quickly move to a suitable layout solution with or without customisations.
Six popular layout options are:
1. Grid Layout
2. Racetrack or Loop Layout
3. Free-Flow Layout
4. Diagonal Layout
5. Angular Layout
6. Hybrid Layout
FAQs
What is retail store layout?
Which layout is used in retail store? Which layout is suited for retail store? Which is the best store layout?
What are the steps of designing retail store layout? How do I create a retail store layout? How can I improve my store layout?
The answers to the above questions can be summarised into one and segregated into two broad stages.
In the first stage, you will have to examine the important factors that will define the requirements of your store layout. An extensive but not exhaustive list of those factors is mentioned below:
· Customers’ Needs and Expectations
· Nature of Products
· Zone Classification
· Product Placement
· Entrance and Exit
· Checkout
· Motion Analysis
· Ratio between Empty and Occupied Space
· Room for Valued-Added and Essential Facilities
· Special Attention to the Differently-Abled
· Hygiene & Maintenance
· Safety and Security
· Schedule Review
Once the store layout requirements are established, you can move to the next stage which is the selection of a layout plan best serving your layout requirements. The selected layout need not necessarily meet all your requirements from where you can go for layout customisation or design something entirely new like a hybrid layout.
For service-related enquiries on retail layout solutions or to discuss layout planning with one of our expert retail consultants, please drop us a message and we will reach out to you.
Retail Healthometer
Check the health of your business? Are you ready to organize & scale ?